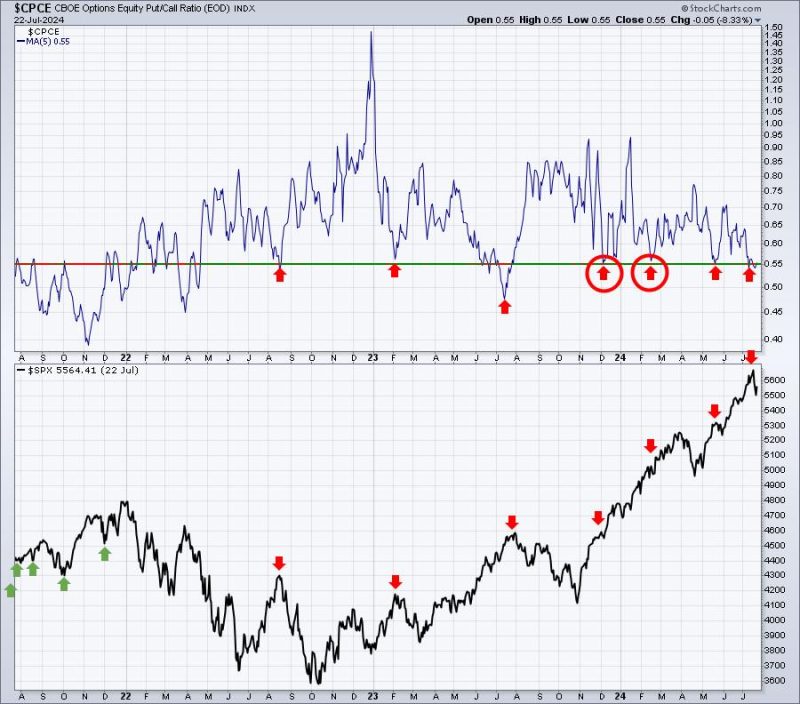
The article you provided discusses important charts to watch when determining whether the market has bottomed out. Based on the information presented, here is a structured and unique version of the article:
Chart 1: S&P 500 Index
The S&P 500 Index is a key indicator of the overall market performance. When analyzing whether the market has bottomed out, closely monitoring the movement of the S&P 500 Index can provide valuable insights. A sustained upward trend in the index can indicate a potential market recovery. On the other hand, a continued decline may suggest that the market has not yet reached its bottom.
Chart 2: Volatility Index (VIX)
The Volatility Index, also known as the VIX, measures market volatility and investor sentiment. During periods of market uncertainty and downturns, the VIX tends to spike as investors become more risk-averse. Monitoring the VIX can help investors gauge the level of fear and uncertainty in the market. A sharp increase in the VIX may signal that the market bottom has not been reached, while a decrease could indicate improving sentiment and a potential market reversal.
Chart 3: Economic Indicators
Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment data, and consumer sentiment can provide crucial information about the health of the economy and the potential direction of the market. During periods of economic instability, these indicators can help investors assess whether the market has hit bottom or if further declines are likely. A strong rebound in economic indicators may suggest that the worst is behind us, while prolonged weakness could indicate continued market turbulence.
In conclusion, monitoring these three key charts – the S&P 500 Index, the Volatility Index, and economic indicators – can help investors determine whether the market has bottomed out. By staying informed and analyzing these indicators, investors can make more informed decisions about their investment strategies during volatile market conditions.